Warning and disclaimer:
If you don't have any basic electronics knowledge, please don't try this one. The author takes no responsibility for any damages caused as a result of this tutorial. Try this one at your own risk.
I am going to use a STC89C52RC microcontroller, a HC-06 UART interface Bluetooth module and a L298N motor driver module to biuld a Bluetooth remote control toy car. The toy car is controlled by Bluetooth Remote Toy, which is an android based application developed by me and can be downloaded form Google play store, so you can remotely control toy car via Bluetooth by your android phone. The toy car commands are as follows.
Every command consists one byte. If you stop a certain action, an OR operation will be performed between that action command and the Stop/Off command. For example,
- 0x01000100(Forward) | 0x00100000(Stop) = 0x01100100, which will be sent to the toy car and make it stop forward.
- 0x01001000(Front light) | 0x00100000(Off) = 0x01101000, which will be sent to the toy car and make it turn off the front light.
The red, green and blue buttons are reserved for those who want to do extra actions.
| Control Function | 1-byte Command |
|---|---|
| Red button | 0x01000001 |
| Green button | 0x01000010 |
| Blue button | 0x01000011 |
| Forward | 0x01000100 |
| Backward | 0x01000101 |
| Right | 0x01000110 |
| Left | 0x01000111 |
| Front light | 0x01001000 |
| Rear light | 0x01001001 |
| Stop/Off | 0x00100000 |
After buying this toy car I have replaced its RF circuit with the 8051 circuit. This toy car has two dc motors at its front and rear side. The front motor is used to control direction (left/right). And the rear motor is used to control the forward and backwards movement. A HC-06 Bluetooth module is used to receive command from android phone. A L298N H-bridge module allows you to control the speed and direction of two DC motors. A STC89C52RC microcontroller is used to control the whole system.
L298N H-bridge module
For more details about this module, please read here. I recommend you read it before you start.
Pin Description
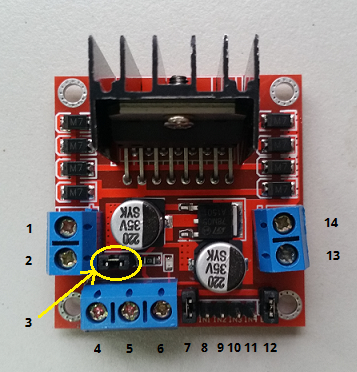
- Front DC motor "+"
- Front DC motor "-"
- 12V jumper - Leave this in place for this tutorial.
- Connect your motor supply voltage here and use between 7 and 12V DC to driver the motors for this tutorial.
- GND
- 5V output - If you're using between 7 and 12V DC to driver the motors and leave 12V jumper in place, the module can also supply your 8051 microcontroller with 5V DC.
- ENA - Front DC motor enable jumper. Leave this in place for this tutorial. If you want to control the speed of the front DC motor you must connect PWM output from your microcontroller to the ENA. For STC89C52RC, there is no PWM output. But you can use timer to implement PWM on 8051 if you want.
- IN1 - Direction of the front DC motor.
- IN2 - Direction of the front DC motor.
- IN3 - Direction of the rear DC motor.
- IN4 - Direction of the rear DC motor.
- ENB - Rear DC motor enable jumper. Leave this in place for this tutorial. If you want to control the speed of the rear DC motor you must connect PWM output from your microcontroller to the ENB. For STC89C52RC, there is no PWM output. But you can use timer to implement PWM on 8051 if you want.
- Rear DC motor "+"
- Rear DC motor "-"
Front motor truth table
| ENB | IN3 | IN4 | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | N/A | N/A | Off |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | Stop |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | Anti-clockwise |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | Clockwise |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | Brake |
Rear motor truth table
| ENA | IN1 | IN2 | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | N/A | N/A | Off |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | Stop |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | Anti-clockwise |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | Clockwise |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | Brake |
It is important to choose the right voltage for your power supply. Too low will result in reduced performance. Too high will cause damage to the motor. Make sure that the voltage does not exceed the voltage rating of your motors. For my toy car, I use two Panasonic NCR18650B 3.6 Volt 18650 batteries connected in series to supply approximately 7.2V. For your toy car, please choose the right voltage for your power supply. It depends on your motors.
Circuit Diagram
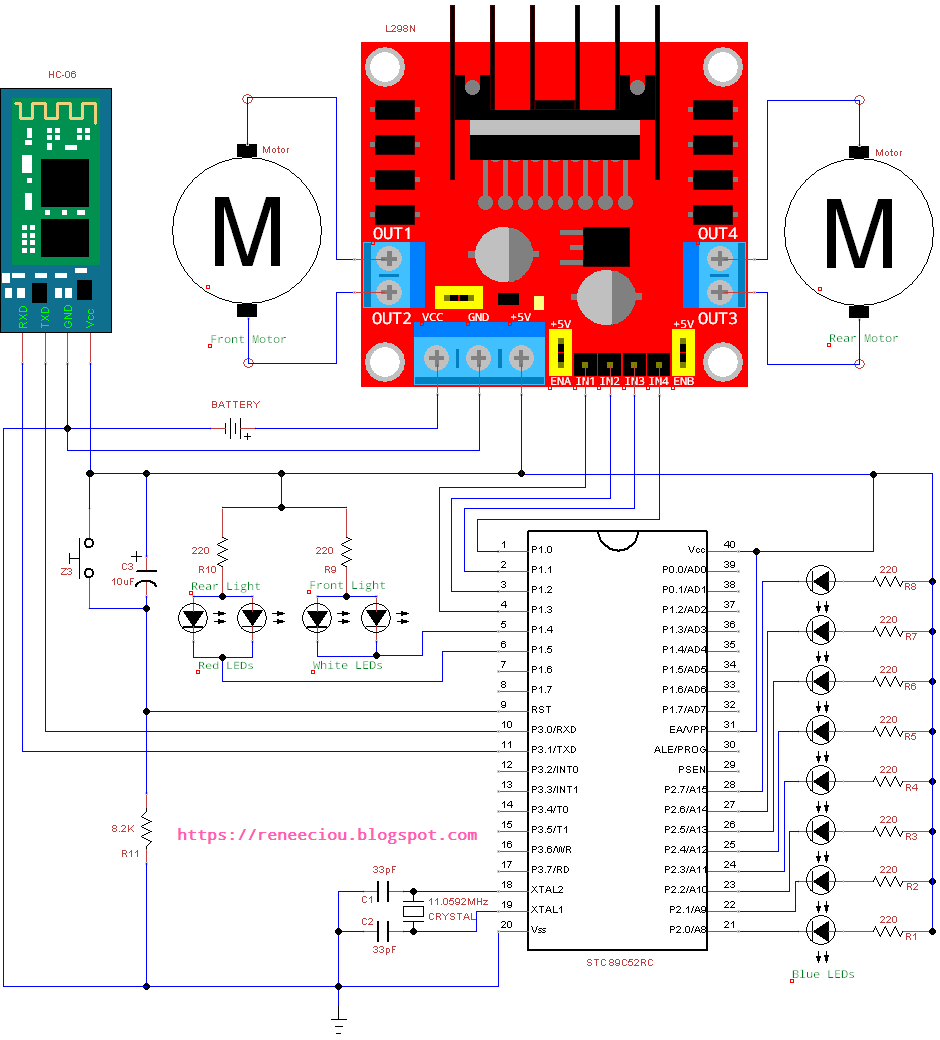
The following toy car is built by myself.






The following code is written in assembly language. You can rewrite it in C language. I think 8051 assembly language is not difficut. Its instruction set is not large so if you are a beginner, you can try to write programs in 8051 assembly language. There will be more understanding of 8051 microcontroller. But if code is more complex and large, and also consider the readability and portability, it is recommended to write code in C language. As for the 8051 development environment, you can refer to here.
Assembly Code
STOP BIT 20H
TURN BIT 21H
R_ON BIT 22H
G_ON BIT 23H
B_ON BIT 24H
B_STP BIT 25H
KP_MV BIT 26H
ORG 00H
AJMP START
ORG 23H ;Serial interrupt vector address
AJMP SERIAL_ROUTINE
ORG 2BH ;Timer2 interrupt vector address
AJMP TIMER2_ROUTINE
START:
ACALL INIT
ACALL INIT_SERIAL
ACALL INIT_TIMER2
LOOP:
ACALL DELAY
JNB B_ON, STOP_BLUE_LED
JB TURN, TURN_AROUND
MOV P2, A
RL A
CJNE A, #01111111B, SET_TURN_RIGHT
SETB TURN
AJMP LOOP
SET_TURN_RIGHT:
AJMP LOOP
TURN_AROUND:
MOV P2, A
RR A
CJNE A, #11111110B, SET_TURN_LEFT
CLR TURN
AJMP LOOP
SET_TURN_LEFT:
AJMP LOOP
STOP_BLUE_LED:
JNB B_STP, RESET_DONE
CLR B_STP
MOV A, #11111110B
CLR TURN
MOV P2, #255
RESET_DONE:
AJMP LOOP
;--------------------
; Delay
;--------------------
DELAY: MOV R6, #100
DLY1: MOV R7, #255
DLY2: DJNZ R7, DLY2
DJNZ R6, DLY1
RET
;--------------------
; Initialize variables
;--------------------
INIT:
MOV SP, #60H
CLR STOP
CLR TURN
CLR R_ON
CLR G_ON
CLR B_ON
CLR B_STP
MOV A, #11111110B
MOV P0, #0
MOV P1, #00110000B
MOV P2, #255
MOV R5, #15
RET
;--------------------
; Initialize serial
;
; TCON Register:
; 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
; TF1 TR1 TF0 TR0 IE1 IT1 IE0 IT0
;
; TMOD Register:
; 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
; GATE1 C/T1# M11 M01 GATE0 C/T0# M10 M00
;
; SCON Register:
; 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
; SM0 SM1 SM2 REN TB8 RB8 TI RI
;--------------------
INIT_SERIAL:
MOV SCON, #50H ;Mode 1: 8-bit UART
MOV TMOD, #20H ;Timer and reload mode
MOV TH1, #0FDH ;Baud rate 9600bps
MOV TL0, #0FDH ;Baud rate 9600bps
SETB TR1 ;Timer1 runs
SETB PS ;High interrupt priority
SETB ES ;Enable serial interrupt
RET
;---------------------------------------------------
; Initialize timer2
;
; T2CON Register:
; 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
; TF2 EXF2 RCLK TCLK EXEN2 TR2 C/T2 CP/RL2
;
; 1 second = 11.0592MHZ / 12 = 921600 = 61440 * 15
; TH2 = (65536-61440)/256 = 16 = 10H
; TL2 = (65536-61440)%256 = 0 = 00H
;
; 0.5 second = 30720 * 15
; TH2 = (65536-30720)/256 = 136 = 88H
; TL2 = (65536-30720)%256 = 0 = 00H
;
; 0.25 second = 15360 * 15
; TH2 = (65536-15360)/256 = 196 = C4H
; TL2 = (65536-15360)%256 = 0 = 00H
;
; IE Register:
; 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
; EA - ET2 ES ET1 EX1 ET0 EX0
;---------------------------------------------------
INIT_TIMER2:
CLR EXF2 ;Reset flag
CLR TCLK ;Disable baud rate generator
CLR RCLK ;Disable baud rate generator
CLR EXEN2 ;Ignore events on T2EX
MOV TH2, #0C4H
MOV RCAP2H, #0C4H
MOV TL2, #00H
MOV RCAP2L, #00H
CLR CT2 ;Timer mode
CLR CPRL2 ;Reload mode
CLR PT2 ;Low interrupt priority
SETB ET2 ;Enable timer2 interrupt
SETB EA ;Global interrupts enable
SETB TR2 ;Timer2 run
RET
;-----------------------------------
; Timer2 interrupt service routine
;
; This is very important for the toy
; car to stop all actions when the
; bluetooth signal of your toy car
; is out of range, and no command
; is received after (0.25 * 2) second.
;
;-----------------------------------
TIMER2_ROUTINE:
PUSH ACC ;Save ACC register on the stack
DJNZ R5, CONTINUE ;Continue timer if it is less then 1 second
JB KP_MV, NO_CLEAR
CLR P1.0 ;Stop forward
CLR P1.1 ;Stop backward
CLR P1.2 ;Stop right
CLR P1.3 ;Stop left
NO_CLEAR:
CLR KP_MV
MOV R5, #15 ;Recount 0.25 second
CONTINUE:
CLR TF2 ;Reset interrupt flag
POP ACC ;Restore ACC
RETI
;----------------------------------------
; Serial port interrupt service routine
;----------------------------------------
SERIAL_ROUTINE:
PUSH ACC
SETB KP_MV
MOV A, SBUF
JNB A.5, RED_BUTTON
SETB STOP
CLR A.5
RED_BUTTON:
CJNE A, #01000001B, GREEN_BUTTON
JB STOP, STOP_RED_BUTTON
SETB R_ON
LJMP EXIT
STOP_RED_BUTTON:
CLR R_ON
CLR STOP
LJMP EXIT
GREEN_BUTTON:
CJNE A, #01000010B, BLUE_BUTTON
JB STOP, STOP_GREEN_BUTTON
SETB G_ON
SJMP EXIT
STOP_GREEN_BUTTON:
CLR G_ON
CLR STOP
SJMP EXIT
BLUE_BUTTON:
CJNE A, #01000011B, FORWARD
JB STOP, STOP_BLUE_BUTTON
SETB B_ON
SJMP EXIT
STOP_BLUE_BUTTON:
CLR B_ON
CLR STOP
SETB B_STP
SJMP EXIT
FORWARD:
CJNE A, #01000100B, BACKWARD
JB STOP, STOP_FORWARD
SETB P1.0
SJMP EXIT
STOP_FORWARD:
CLR P1.0
CLR STOP
SJMP EXIT
BACKWARD:
CJNE A, #01000101B, RIGHT
JB STOP, STOP_BACKWARD
SETB P1.1
SJMP EXIT
STOP_BACKWARD:
CLR P1.1
CLR STOP
SJMP EXIT
RIGHT:
CJNE A, #01000110B, LEFT
JB STOP, STOP_RIGHT
SETB P1.2
SJMP EXIT
STOP_RIGHT:
CLR P1.2
CLR STOP
SJMP EXIT
LEFT:
CJNE A, #01000111B, CAR_FRONT_LIGHT
JB STOP, STOP_LEFT
SETB P1.3
SJMP EXIT
STOP_LEFT:
CLR P1.3
CLR STOP
SJMP EXIT
CAR_FRONT_LIGHT:
CJNE A, #01001000B, CAR_REAR_LIGHT
JB STOP, STOP_FRONT_LIGHT
CLR P1.4
SJMP EXIT
STOP_FRONT_LIGHT:
SETB P1.4
CLR STOP
SJMP EXIT
CAR_REAR_LIGHT:
CJNE A, #01001001B, EXIT
JB STOP, STOP_REAR_LIGHT
CLR P1.5
SJMP EXIT
STOP_REAR_LIGHT:
SETB P1.5
CLR STOP
EXIT:
CLR RI
POP ACC
RETI
END
Demo
Warning and disclaimer:
If you don't have any basic electronics knowledge, please don't try this one. The author takes no responsibility for any damages caused as a result of this tutorial. Try this one at your own risk.
沒有留言:
不接受新意見。